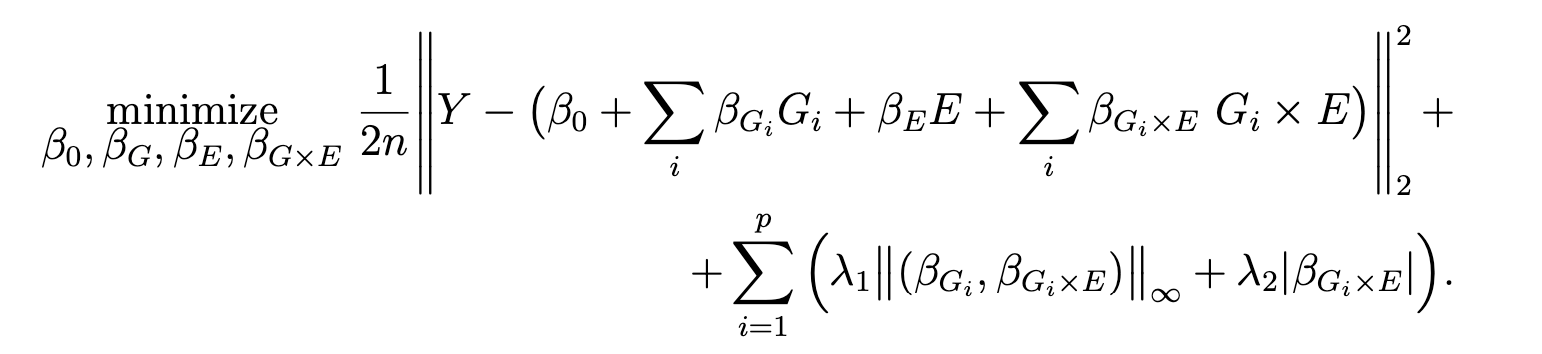
The package is developed to fit a regularized regression model that we call gesso for the joint selection of gene-environment (GxE) interactions. The model focuses on a single environmental exposure and induces a “main-effect-before-interaction” hierarchical structure. We developed and implemented an efficient fitting algorithm and screening rules that can discard large numbers of irrelevant predictors with high accuracy.
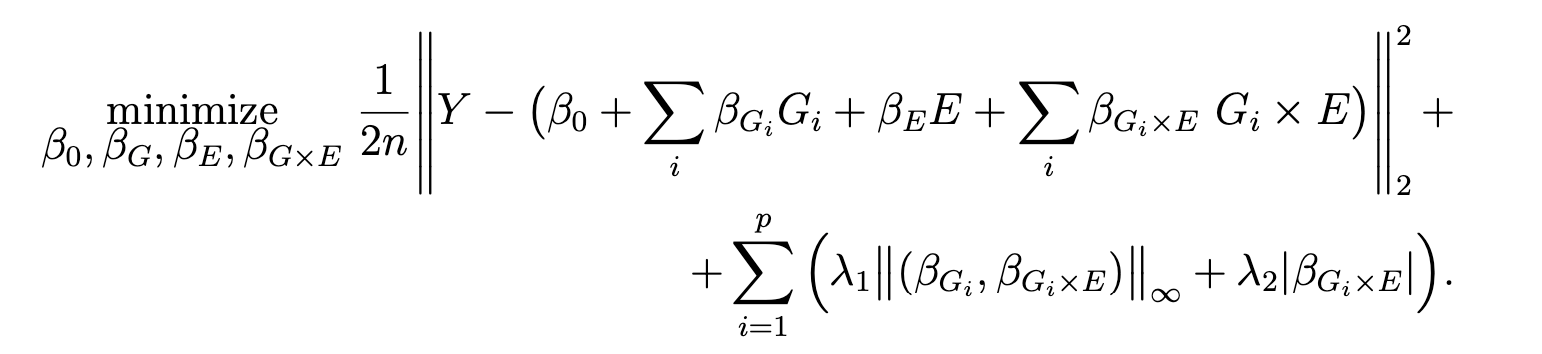
gesso model induces hierarchical selection of the (GxE) interaction terms via overlapped group lasso structure. The model has two tuning parameters λ1 and λ2 allowing flexible, data dependent control over group sparsity and additional interactions sparsity.
gesso package can be used
The package supports sparse matrices dgCMatrix and
(filebacked) bigmatrix format from the bigmemory package
for large or out of RAM datasets.
Tha package allows to add unpenalized covariates to the model.
For more information and examples please see package vignette.
## install.packages("devtools")
library(devtools)
devtools::install_github("NataliaZemlianskaia/gesso")library(gesso)
## generate the data: 400 main effects and 400 interaction effects
## with 10 non-zero main effects and 5 non-zero interaction effects, sample size equal to 150
data = data.gen(sample_size=150, p=400,
n_g_non_zero=10, n_gxe_non_zero=5,
family="gaussian", mode="strong_hierarchical")
## tune the model over a 2D grid of hyperparameters
tune_model = gesso.cv(data$G_train, data$E_train, data$Y_train,
grid_size=20, tolerance=1e-4,
parallel=TRUE, nfold=4,
normalize=TRUE, normalize_response=TRUE,
seed=1)
## obtain interaction and main effect coefficietns corresponding to the best model
coefficients = gesso.coef(fit=tune_model$fit, lambda=tune_model$lambda_min)
gxe_coefficients = coefficients$beta_gxe
g_coefficients = coefficients$beta_g
## check if all non-zero features were recovered by the model
cbind(data$Beta_GxE[data$Beta_GxE != 0], gxe_coefficients[data$Beta_GxE != 0])
## [,1] [,2]
## [1,] -1.5 -0.9711450
## [2,] -1.5 -1.9493914
## [3,] -1.5 -0.5148486
## [4,] -1.5 -1.4827039
## [5,] 1.5 1.8539925
## check if the largest estimated interaction effects correspond to the true non-zero coefficients
(data$Beta_GxE[order(abs(gxe_coefficients), decreasing=TRUE)])[1:10]
## [1] -1.5 1.5 -1.5 1.5 -1.5 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
## calculate principal selection metrics
selection = selection.metrics(true_b_g=data$Beta_G,
true_b_gxe=data$Beta_GxE,
estimated_b_g=g_coefficients,
estimated_b_gxe=gxe_coefficients)
cbind(selection)
## selection
## b_g_non_zero 77
## b_gxe_non_zero 63
## mse_b_g 0.2775684
## mse_b_gxe 0.5617425
## sensitivity_g 1
## specificity_g 0.8282051
## precision_g 0.1298701
## sensitivity_gxe 1
## specificity_gxe 0.8531646
## precision_gxe 0.07936508
## auc_g 0.999999
## auc_gxe 0.999998 ”A Scalable Hierarchical Lasso for Gene-Environment Interactions” Natalia Zemlianskaia, W.James Gauderman, Juan Pablo Lewinger
https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13510